An Individualized Education Program (IEP) Progress Report is a tool for monitoring a student’s progress toward their IEP goals. It ensures that students with disabilities receive the necessary support while holding schools accountable for their role in the process.
These reports provide valuable insights into a student's growth and help the IEP team make informed decisions to tailor instruction and support.
Key Features of an IEP Progress Report
- Follow IDEA Requirements: Schools are legally obligated under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) to monitor and report progress on IEP goals.
- Provides Data-Driven Insights: Progress reports utilize measurable data—like test results, observations, or work samples—to demonstrate whether students are meeting their goals.
- Promotes Accountability: Teachers, therapists, and other team members rely on the report to ensure they are delivering appropriate support.
- Strengthens Collaboration: The report keeps educators, therapists, and families on the same page.
Why Are IEP Progress Reports Important?
1. Tracking Progress
IEP Progress Reports actively measure how students are advancing toward their goals. They highlight what’s working and pinpoint areas where adjustments are needed.
2. Ensuring Accountability
Schools fulfill their legal responsibility under IDEA by providing progress updates to parents. These reports hold educators and schools accountable for delivering appropriate support and maintaining transparency.
3. Guiding Informed Decisions
Progress reports equip IEP teams with accurate, data-driven insights. This information helps teams adjust goals, refine strategies, and implement targeted supports to meet each student’s unique needs.
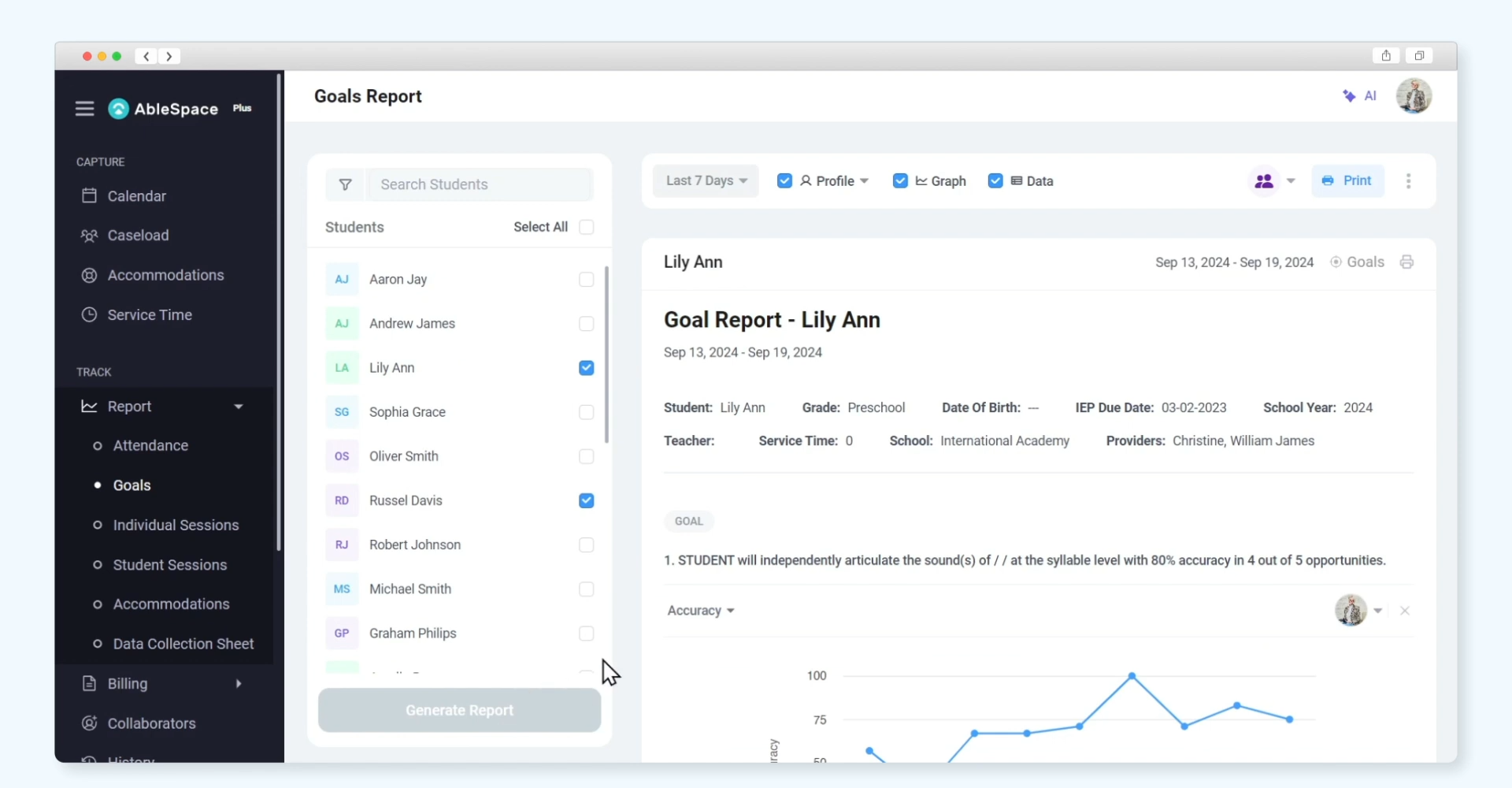
Components of an Effective IEP Progress Report
1. SMART IEP Goals
Clearly defined goals that follow the SMART framework—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound—are the foundation for tracking progress.
2. Baseline Data
Establish a starting point for each goal to measure the student’s growth and progress over time accurately.
3. Progress Status Indicator
Use clear, easy-to-understand statuses to show progress:
- Met: The goal has been successfully achieved.
- In Progress: Progress is being made, but the goal is not yet fully met.
- Not Met: Little to no progress observed, indicating a need for adjustments.
4. Objective Evidence
Back up progress with measurable and concrete data, such as:
- Test scores
- Work samples
- Observation notes
5. Actionable Recommendations
Provide specific suggestions to improve outcomes, such as modifying instruction methods, increasing support, or implementing additional accommodations tailored to the student’s needs.
How Often Should IEP Progress Reports Be Sent?
The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) requires schools to issue IEP Progress Reports as frequently as general report cards. This ensures that families receive regular updates on their child’s progress in alignment with the academic reports provided for other students
Steps to Write an IEP Progress Report
Step 1: Review the IEP Goals
Begin by reviewing each student’s goals to ensure alignment.
Step 2: Gather Data
Collect objective data through:
- Assessments and standardized tests
- Observation notes
- Work samples
- Input from other team members
Step 3: Use Measurable Language
Avoid vague terms like "improved" or "better." Use measurable language instead:
- Example: "John can complete 3 out of 5 math problems independently."
Step 4: Provide Examples
Include specific examples of performance in the IEP progress report:
- "Mary used scissors to cut along a straight line with 75% accuracy."
Step 5: Offer Recommendations
If the student is not meeting goals, propose adjustments such as:
- Modifying goals
- Changing instructional methods
- Adding accommodations or interventions
Best Practices for Writing IEP Progress Reports
- Use Clear, Jargon-Free Language: Reports should be easy for parents to understand.
- Focus on Measurable Data: Rely on evidence rather than subjective opinions.
- Highlight Strengths and Needs: Acknowledge growth while identifying areas for improvement.
- Include Visual Aids: Graphs or charts can help visualize progress in IEP progress reports.
- Collaborate with Team Members: Inputs from specialists, therapists, and teachers ensures accuracy.
Common Challenges in IEP Progress Reporting and How to Overcome Them
1. Inconsistent Data Collection
Solution: Use IEP data-tracking tools to streamline data collection, analysis, and monitoring.
2. Vague Language
Solution: Stick to specific and measurable language.
3. Misalignment with Goals
Solution: Review goals regularly to ensure alignment with reports.
4. Time Management
Solution: Schedule regular intervals to gather data and draft reports.
How to Streamline Progress Reporting with Digital IEP Software?
Progress reporting is important in special education, but it can be overwhelming for educators managing multiple responsibilities.
While pre-made Goal Tracking Forms and IEP progress report templates provide a foundation, they often fall short. Such tools fail to meet the demands of real-world special education environments. Here are the most common challenges SPED teachers face when they use IEP goal tracking forms or progress report templates::
- Time-consuming setup
- Fragmented data storage
- Limited customization
- Manual updates
This is where AbleSpace–a dedicated special education software for caseload management–helps by simplifying and largely automating the entire process. This software features seamless goal tracking and IEP progress report generation capabilities tailored for special education programs.
Special education teachers, therapists, and paraprofessionals deserve tools like AbleSpace that reduce administrative burdens and let them focus on what matters most: supporting differently-abled students in realizing their true potential.
AbleSpace not only simplifies progress tracking and reporting but also enhances the overall efficiency of the IEP process by -
- Automating routine tasks to save time
- Reducing errors and inconsistencies with centralized data storage and tracking
- Improving communication with parents and IEP teams
- Ensuring compliance with IDEA guidelines
You can start your free trial of AbleSpace today and discover how it can help you save hours of labor every week.
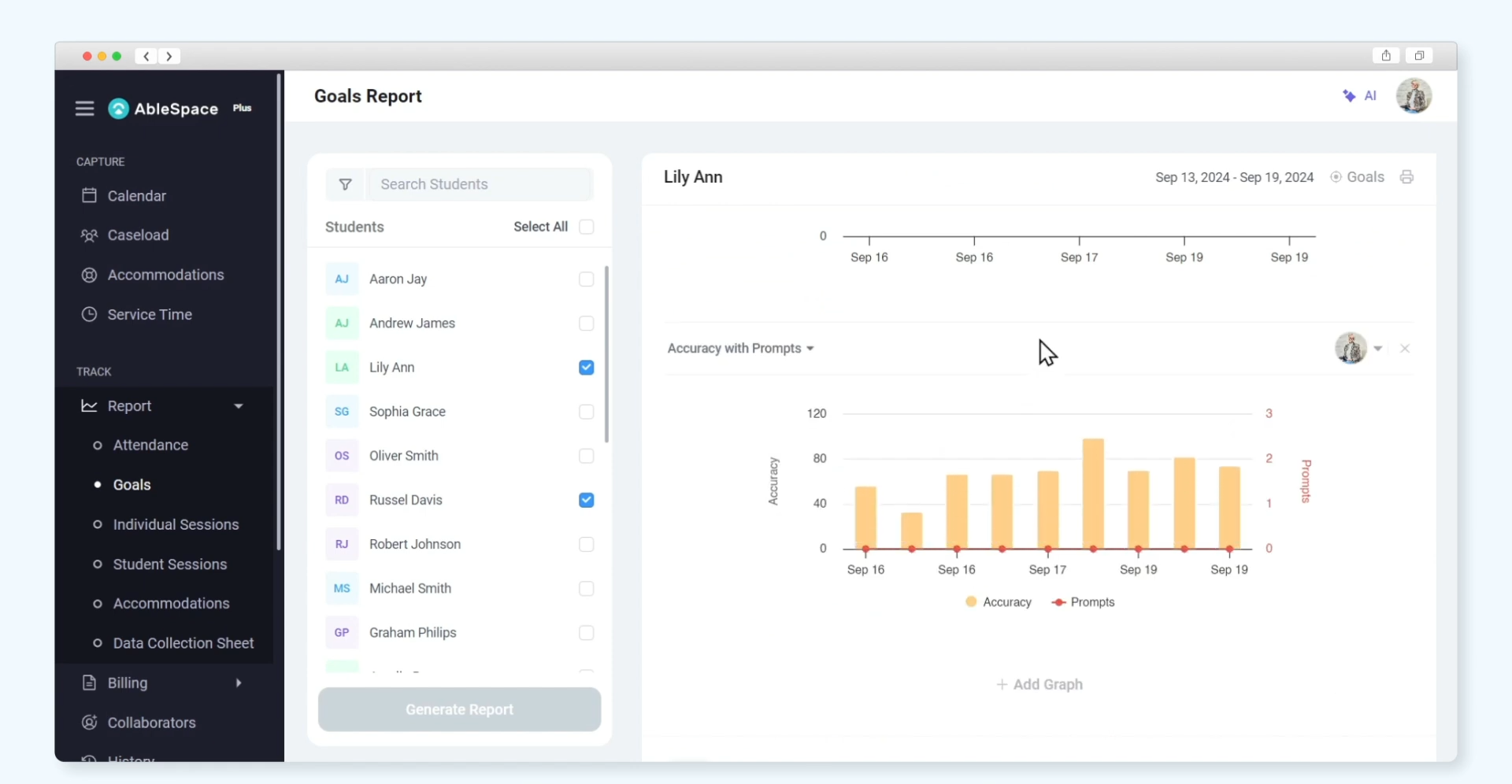
IEP Progress Report Examples
1. Reading Fluency
Goal: "Sam will read 3rd-grade-level texts with 90% accuracy in 4 out of 5 trials."
Progress:
- Baseline: 70% accuracy recorded in August.
- Current Status: Sam achieved 85% accuracy on the most recent assessment.
- Data: Weekly reading logs and comprehension quizzes indicate consistent improvement.
- Recommendation: Continue small group reading instruction and introduce new comprehension strategies to further progress.
2. Writing Skills
Goal: "Lila will write a five-sentence paragraph with proper punctuation in 3 out of 4 attempts."
Progress:
- Baseline: In the beginning, Lila could write two sentences with 50% punctuation accuracy.
- Current Status: Lila now consistently writes three sentences with correct punctuation in 3 of 4 attempts.
- Data: Work samples and teacher observations demonstrate improvement in sentence length and punctuation accuracy.
- Recommendation: Prioritize expanding Lila's vocabulary and incorporating practice with sentence starters to further develop her writing skills.
3. Math Problem Solving
Goal: "Eli will solve two-step word problems with 80% accuracy over 4 consecutive trials."
Progress:
- Baseline: 50% accuracy in September.
- Current Status: Eli has improved to 75% accuracy on practice worksheets.
- Data: Weekly math assessments and class activities indicate steady progress.
- Recommendation: Provide visual aids, such as number lines or diagrams, to enhance Eli's problem-solving skills.
4. Social Interaction
Goal: "Mia will initiate peer interactions in structured activities 3 times weekly."
Progress:
- Baseline: Mia initiated interactions only once every two weeks.
- Current Status: Mia now initiates interactions twice weekly during group projects.
- Data: Teacher observations and peer feedback confirm consistent effort on Mia’s part to engage with peers..
- Recommendation: Encourage participation in more structured group games to build confidence.
5. Fine Motor Skills
Goal: "Jonah will use scissors to cut out basic shapes with 80% accuracy in 3 out of 5 trials."
Progress:
- Baseline: Jonah struggled with grip and could cut straight lines with 50% accuracy.
- Current Status: Jonah has achieved 75% accuracy in cutting circles and triangles.
- Data: Work samples from art class show marked improvement in precision and control.
- Recommendation: Incorporate fine motor exercises into daily activities, like beading and tracing.
6. Behavior Regulation
Goal: "Emma will use a self-regulation strategy (e.g., deep breathing) to calm down during stressful situations 4 out of 5 times."
Progress:
- Baseline: Emma needed teacher prompts to use any strategy.
- Current Status: Emma independently uses deep breathing in 3 out of 5 stressful situations.
- Data: Daily behavior logs show a reduction in emotional outbursts.
- Recommendation: Reinforce the use of visual reminders and provide opportunities to practice self-regulation strategies during calm moments.
7. Adaptive Skills
Goal: "Ben will independently put on his coat and zip it up within 2 minutes in 4 out of 5 opportunities."
Progress:
- Baseline: Ben required full assistance to complete the task.
- Current Status: Ben completes the task independently in 3 out of 5 opportunities.
- Data: Notes from teacher and paraprofessional highlight significant progress.
- Recommendation: Practice zipping skills during transition times to reinforce independence.




